ABSTRACT
-
Background
- We aimed to examine the feasibility of intensive lifestyle habituation with a subsequent home program, including forest-based exercise, as an alternative approach to conventional cardiac rehabilitation for both primary and secondary prevention of coronary artery disease (CAD).
-
Methods
- A total of 28 participants were included in a 1-week intensive education program aimed at fostering desirable lifestyle habits in the study: 17 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention and 11 participants at high risk of CAD. Subsequently, they engaged in a self-directed, home-based program that included unstructured exercise in an urban forest. The terrain of the urban forest was analyzed to estimate metabolic equivalent levels and to assess safety and accessibility for patient exercise.
-
Results
- Throughout the program, no adverse cardiac events were reported. Additionally, risk factors for CAD—including body composition, blood sugar levels, hemodynamic variables, total cholesterol levels, and cardiorespiratory endurance—showed significant improvement in both groups.
-
Conclusions
- Intensive lifestyle habituation and unstructured, self-directed exercise in the forest were as effective and safe as conventional cardiac rehabilitation for patients with CAD. The study demonstrated that an urban forest could serve as a safe exercise environment in both primary and secondary prevention strategies for CAD.
-
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Forests; Exercise; Cardiac rehabilitation; Walking
INTRODUCTION
- Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, posing a significant threat to public health. Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) has been shown to be effective in preventing both the initial onset and recurrence of cardiovascular diseases [1,2]. The aim of a CR program is to prevent the recurrence of cardiovascular diseases while improving cardiovascular function and physical fitness through the management and improvement of cardiovascular risk factors [3]. Furthermore, CR is recognized for its ability to either delay the progression of the disease or improve clinical outcomes by simultaneously optimizing patient’s physical, psychological, professional, and social capabilities [4].
- Conventional hospital-based CR typically involves three sessions per week over a 12-week period. However, several barriers prevent regular attendance at these programs, which is a concern for many rehabilitation professionals. In fact, less than 20% of all cardiac patients discharged from the hospital in the United States attend CR [5]. One significant barrier is the difficulty of traveling long distances between home and the hospital [6]. Consequently, home-based CR was proposed as an alternative. Studies have shown that home-based CR is not inferior to hospital-based rehabilitation in terms of safety and effectiveness [7]. Additionally, a new concept of intensive CR has been developed to enhance program efficiency. Intensive CR has proven to be an effective alternative, addressing the limitations of conventional CR with intense, multidimensional interventions over a relatively short period [8]. CR involves a multidisciplinary approach, with exercise serving as a central component of the program. Therefore, for patients who opt for home-based rehabilitation, it is crucial to find a suitable exercise environment near their home. Furthermore, strong motivation is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle in these patients.
- Forest healing has been gaining attention for over a decade in Korea. Although forests as an orographic area comprise more than 60% of the territory in Korea, the initiation of forest healing occurred later compared to other countries, leaving both theoretical and practical foundations yet to be fully developed. In contrast, European countries like Germany and Switzerland have a long history of utilizing their forests for therapeutic purposes. Japan has also shown interest in leveraging its forests for health promotion [9,10].
- Factors related to forest healing produce therapeutic effects in forest environments. These factors encompass various environmental elements from the forest, such as phytoncides, visual stimuli, distinctive sounds, abundant oxygen and anions, as well as optimal temperature, humidity, and terrain [11]. Numerous studies have sought to evaluate the impact of these factors on health improvement; however, many aspects remain unconfirmed.
- The major effects of forest healing identified in previous studies include improvements in psychoemotional stability and recovery, autonomic nervous and hormonal activities, immune functions, and cardiovascular conditions. Emotional disorders such as depression, anxiety, and anger have shown improvement following forest therapy programs [12]. Improvements in heart rate variability and alpha waves in electroencephalography, along with decreased cortisol levels and attenuated hemodynamic variables, have been reported after participation in forest healing programs [13,14]. These results do not appear to act independently but are likely correlated with each other. However, the detailed mechanisms behind these improvements require further exploration in future studies. Other research has indicated that phytoncides, released in large quantities from forest environments, enhance the activity and proliferation of natural killer cells and stimulate the expression of anticancer proteins [15]. Despite these findings, comprehensive studies clarifying the effects of forest environments on controlling specific diseases remain limited.
- Given the recent emergence of alternative approaches to conventional CR and the advocacy for forests as healing environments, we explored the practicality of a new CR method that combines intensive lifestyle habituation with subsequent home-based programs, which include exercising in urban forests. Additionally, we focused on assessing the feasibility and safety of exercising in urban forests for both primary and secondary prevention of coronary artery disease (CAD).
METHODS
- Ethics statement
- The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Kangbuk Samsung Hospital (No. 2022-06-054). The study was thoroughly explained to the patients, who fully understood all the processes involved and voluntarily chose to participate.
- Participants
- Eleven older adults at risk for CAD were recruited from a health center in Seosan, Korea, through advertisements targeted at the local community. Seventeen patients who had undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for CAD were recruited from Kangbuk Samsung Hospital (Seoul, Korea) by advertising to outpatients, and were included in a secondary prevention group. Eligibility for the primary prevention group included older adults without cardiac disease but with risk factors for CAD. For the secondary prevention group, eligibility was limited to patients classified as low or moderate risk according to the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation (AACVPR) stratification criteria (Table 1).
- Procedures
- Intensive lifestyle education was conducted 1 week prior to the commencement of the home-based program for both groups, as shown in Fig. 1. The primary prevention group participated in residential intensive lifestyle education at the National Center for Forest Therapy (Yeongju, Korea). Meanwhile, the secondary prevention group's lifestyle education was held at The K Hotel, which is surrounded by an urban forest and located in the southern part of Seoul, Korea. A multidisciplinary team, including a medical doctor, program coordinator, exercise physiologist, nutritionist, chef, and psychologist, was present to oversee patient education. The daily schedule for all patients included both theoretical and practical education, encompassing exercise classes, nutritional education with cooking demonstrations, and stress management sessions. These activities were designed to promote regular physical activity, a prudent diet, and emotional control, all aimed at modifying CAD risk factors. Forest trails were utilized by both groups to acquaint the patients with forest-based exercises, as depicted in Figs. 2 and 3. Additionally, indoor exercises involving equipment such as gym balls and elastic bands were introduced, which the patients were encouraged to continue during the home-based program.
- After 1 week of intensive lifestyle education, participants independently began an 11-week home-based program, building on the lessons they had learned. They were encouraged to maintain regular exercise both in the forest and at home, adhere to a low-sodium and low-fat diet, and practice stress management as part of their daily routine. Participants were equipped with wearable devices (Google Fitbit) to track daily energy expenditure and monitor heart rate. Both groups were informed about their target heart rate ranges. Staff members kept track of daily activities by communicating with patients via smartphones. To monitor the progression of the program and the clinical status of the patients, staff accompanied them on weekly forest hikes. During these hikes, a staff member carried a portable automated external defibrillator to manage any potential cardiac incidents.
- Statistical analysis
- Topographic analysis was prioritized to ensure the forest was a safe exercise environment for both post-PCI patients and primary group participants. Devices including the Garmin 65s (Garmin Ltd), Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Samsung), and iPhone 13 Pro (Apple) were utilized to measure the forest trail's topography, capturing details such as altitude, slope, and distance. These measurements were processed using software like QGIS (https://www.qgis.org/en/site/) and Global Mapper (Blue Marble Geographics) to produce more detailed data. To determine the metabolic equivalent (MET) level corresponding to the terrain conditions in the forest, we employed the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) metabolic equation. This equation estimated the relative oxygen consumption (VO2, mL/kg/min) by factoring in the patients’ walking speed and the trail gradient. Walking speeds were set at 2, 3, and 4 km/hr, tailored to the patients’ abilities and aligned with their individual target heart rates. The target heart rate was established at 40% to 59% of heart rate reserve (HRR) for moderate intensity in the secondary group and 60% to 70% of HRR for vigorous intensity in the primary group (Table 2). During the forest exercise sessions, staff members vigilantly monitored the patients for any adverse events, including heart attack or arrest, syncope or dizziness, severe dyspnea, serious arrhythmia, hypoglycemia, intermittent claudication, and significant fatigue.
- We conducted 2×2 (time×group) repeated measures analysis of variance to examine the within- and between-group differences in body composition, cardiometabolic variables, and functional capacity after 12 weeks of the primary and secondary preventive program. Quantitative data were presented as mean±standard deviation. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
- The demographic characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 1. Estimated MET levels for the forest terrain are presented in Tables 3 and 4. In the primary prevention group, the average MET levels at walking speeds of 2, 3, and 4 km/hr were approximately 4.30, 5.91, and 7.60, respectively (Table 3). In contrast, the secondary prevention group recorded average METs of 3.65, 4.98, and 6.31, respectively (Table 4). During the 12-week period of forest trakking and home exercise, there were no unexpected cardiovascular emergencies, with the exception of hypoglycemia and leg pain in the secondary prevention group, as detailed in Table 5. The primary prevention group experienced no cardiac events or discomfort throughout the program.
- Changes in body composition, hemodynamic variables, blood lipids, blood glucose, inflammation indicators, and functional capacity are listed in Table 6. Both groups experienced significant decreases in body weight and percentage body fat, with no significant differences between the groups. Muscle mass remained unchanged in both groups. Systolic blood pressure showed significant changes in both groups, with the primary prevention group demonstrating statistical superiority. Diastolic blood pressure exhibited slight changes in both groups, but these were not significantly different between the groups. Both resting and maximal heart rates decreased significantly in both groups, again with no significant differences between the groups. Levels of total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) decreased significantly in both groups. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels also changed significantly, particularly in the primary group, though no differences were noted between the groups. Triglyceride levels did not show a statistical difference either within or between the groups, despite an apparent decrease. Fasting blood glucose levels remained relatively stable, showing no meaningful changes within or between the groups, although a slight change in glycosylated hemoglobin was statistically significant. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels differed between the two groups, with no significant changes within the groups in terms of MET level. The Framingham risk score (FRS) changed significantly, particularly in the primary group, but no significant difference was observed between the groups.
DISCUSSION
- The ACSM metabolic equation effectively assesses level and uphill conditions but cannot be directly applied to estimate oxygen consumption or MET levels on downhill terrain. The energy cost of downhill walking slightly decreases compared to level walking until the downhill grade reaches –30%. Beyond this point, the energy cost exceeds that of level walking [16]. Since all the downhill grades of the forest terrain for both primary and secondary prevention in this study did not exceed –30%, the calculated average MET level might be slightly overestimated. Thus, the average MET level should be considered an approximate value.
- For the primary prevention group, the target heart rate was set between 60% and 70% of HRR, which is considered vigorous intensity. This intensity level corresponded to a walking speed of 3 km/hr during forest hiking in the primary prevention program. The estimated MET level at this walking speed was approximately 5.91. Given the average age of participants in the primary prevention group, this activity level was categorized as vigorous intensity. During the forest hiking, no cardiac events or discomforts were reported in this group, suggesting that the forest terrain, which facilitated a vigorous activity level of 5.91 METs, provided a safe environment for the participants.
- In contrast, the target heart rate for the secondary prevention group was set at 40% to 59% of HRR, which corresponds to moderate intensity. This was consistent with a walking speed of 3 km/hr during forest hiking. The estimated MET level at this walking speed was approximately 4.98. Although this MET level was lower, the forest hiking under these conditions was unlikely to be stressful enough to cause adverse cardiovascular events in the secondary prevention group. No serious cardiac events were reported, except for intermittent claudication and one case of hypoglycemia. However, these incidents were not directly attributable to the level of physical activity during forest hiking.
- Overweight and obesity are significant global health concerns. This study observed desirable changes in body composition that align with findings from other research [17], showing that participants in both groups adhered to a physical activity regimen that was effective in achieving a negative energy balance through forest-based exercises.
- Regarding the impact of exercise on lipid profiles, regular physical activity can lead to a reduction in triglyceride levels by approximately 16%–19%. Studies have also shown significant improvements in total cholesterol, LDL-C, and HDL-C levels following aerobic exercise interventions. However, some studies have reported conflicting results concerning the effects of exercise on lipid profiles, particularly in relation to total and LDL-C levels.
- In the current study, we observed a significant decrease in total cholesterol, likely due to the cumulative effect of reductions in other lipid components, although these individual reductions did not reach statistical significance [18–20]. The baseline concentrations of these lipids in the secondary prevention group were within normal ranges, likely influenced by the use of lipid-lowering medications by most participants. Despite these already low baseline concentrations, all lipid parameters decreased during the study period, suggesting that the patients' adherence to a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, played a role in these improvements. Exercise interventions have been shown to induce favorable changes in lipid profiles and glycemic control among individuals with diabetes [21–23]. Although there is some variability in the results of these studies, regular physical activity continues to be a fundamental aspect of diabetes management and cardiovascular risk reduction [24–27]. The inflammatory marker synthesized in the liver in response to interleukin 6, hs-CRP, is significant as it can predict mortality related to cardiovascular disease [28–30]. Exercise, including aerobic, resistance, and complex routines, has been demonstrated to improve hs-CRP levels, with moderate-intensity exercise being particularly effective in managing this marker and preventing cardiovascular disease [31]. However, a combined exercise program targeting older women over the age of 70 years did not result in statistically significant changes in blood lipids (total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL-C) and hs-CRP levels [32,33].
- In our study, the baseline concentration of hs-CRP was 1.16 mg/L in the primary prevention group and 0.4 mg/L in the secondary prevention group. The relatively low level of hs-CRP in the secondary prevention group was likely influenced by the medications they were taking. Despite this, no significant changes were observed in hs-CRP levels in either group, suggesting that factors other than medication may have been involved.
- Maximal functional capacity, an indicator of cardiorespiratory fitness, is crucial for performing prolonged exercise or physical activity and is linked to reduced mortality from various causes, including CAD [34,35]. Research has shown that improving cardiopulmonary fitness by 1 MET can decrease the incidence of cardiovascular disease by 25% and increase survival rates by 16% [36–38].
- In our study, both the primary and secondary prevention groups demonstrated significant improvements in functional capacity, with increases of 1.1 and 2.3 METs, respectively. These findings suggest that unstructured voluntary exercise in urban forests is as effective as structured hospital-based exercise programs in enhancing prognosis and survival rates [39–43]. Additionally, we observed a significant reduction in resting heart rate in both groups, which is advantageous for CAD patients as it lowers the cardiac workload. The reduction in resting heart rate can likely be attributed to regular exercise and physical activity, as well as the impact of beta-blocking agents, which were administered to most patients in the secondary prevention group. In our study, the FRS score decreased by 4.7 in the primary prevention group. This decrease is encouraging, reflecting improvements in physical composition, cardiovascular metabolism-related variables, and physical strength variables, as previously discussed. Although the decrease was not statistically significant in the secondary prevention group, the observed downward trend is still considered beneficial in promoting regular physical activity among patients with CAD. The FRS serves as a foundation for demonstrating the effectiveness of our program in several of the variables that were investigated.
- To address the limitations of conventional CR programs, which often include issues with accessibility and insufficient intensity, we developed a program that integrates elements of both home-based and intensive CR. Our approach was designed to capitalize on the advantages of each modality while mitigating their respective drawbacks. A distinctive aspect of our program is the utilization of urban forests near patients' residences as a setting for exercise.
- Our study demonstrated that the blended rehabilitation approach was as effective as traditional rehabilitation programs. Additionally, the urban forest setting was found to be convenient and suitable for participants engaged in both primary and secondary prevention programs, regardless of the known therapeutic benefits associated with forest environments. The success of our program was notably enhanced by a strong focus on intensive lifestyle modification, which was crucial in motivating patients to adopt and maintain healthy habits in their daily lives. However, the study revealed that the amount of exercise conducted in the forest setting was insufficient each week. Specifically, a limitation was observed in monitoring the exact amount of physical activity (kilocalories per week) due to challenges in controlling diet, psychological factors, and physical activity. Despite these challenges, implementing outdoor exercise in forest environments represents a significant and innovative approach to rehabilitation programs. Therefore, the program is both feasible and safe, and it has the potential to yield positive outcomes.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization: KSC, DSY; Data curation: JYL; Formal analysis: KCJ; Investigation: KCJ; Methodology: JYL; Validation: JYL; Writing–original draft: JYL, KCJ; Writing–review & editing: KSC, DSY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflicts of interest
Jong-Young Lee is an Editorial Board member of Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy, but was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Forestry Promotion Institute (Seoul, Korea).
Fig. 1.Intensive lifestyle education program. CPR, cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
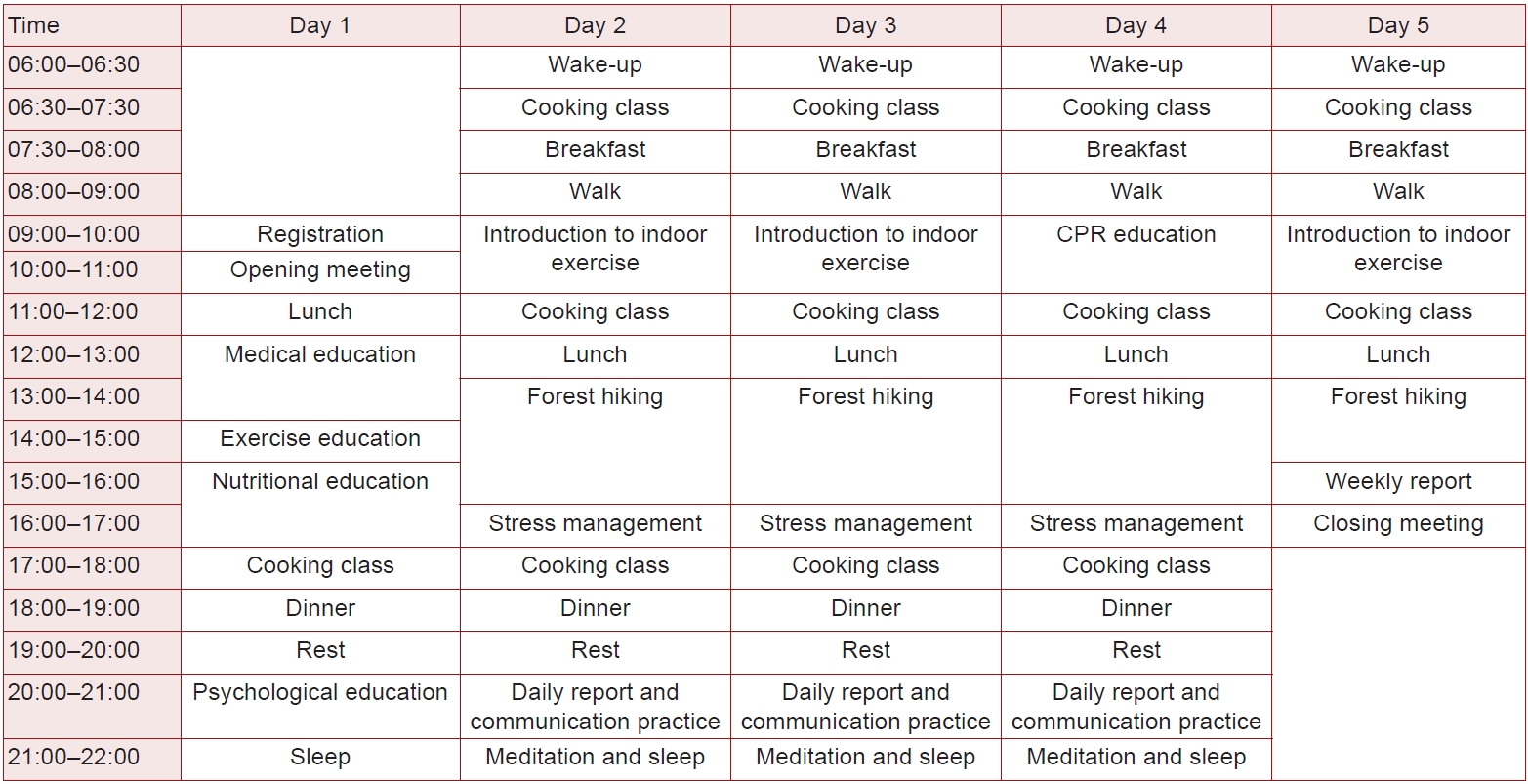
Fig. 2.Contour map of Seosan, Korea, for the primary prevention group.
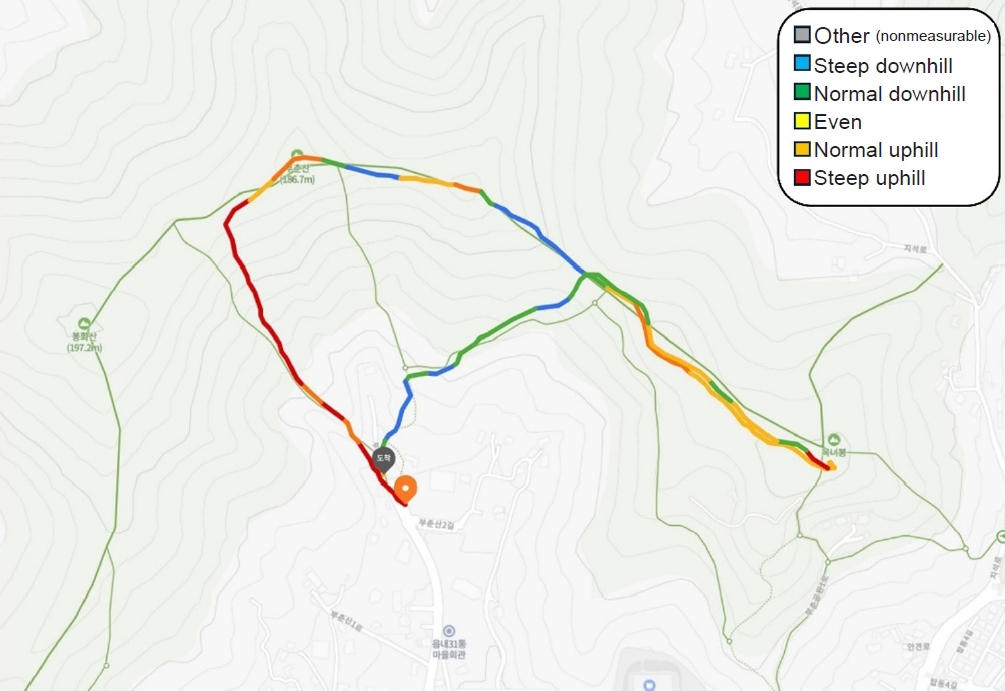
Fig. 3.Contour map of Ansan, Korea, for the secondary prevention group.

Table 1.Patient demographics (n=28)
|
Characteristic |
Primary prevention group (n=11) |
Secondary prevention group (n=17) |
|
Age (yr) |
67.9±8.3 |
63.1±9.8 |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
Female |
9 |
4 |
|
Male |
2 |
13 |
|
Height (cm) |
158±7.3 |
164±8.4 |
|
Weight (kg) |
63.9±8.4 |
69±13.2 |
|
Clinical status |
Hypertension, 54.5% |
Post-PCI for coronary artery disease (chronic coronary syndrome, 50%; acute coronary syndrome, 50%) |
|
Diabetes mellitus, 54.5% |
|
|
Hyperlipidemia, 81.8% |
|
Table 2.Exercise intensity range
|
Exercise intensity |
Relative intensity |
Absolute intensity (MET) |
|
HRR (%) |
RPE |
Young (20–39 yr) |
Middle age (40–64 yr) |
Older (≥65 yr) |
|
Very light |
<30 |
<9 |
<2.4 |
<2.0 |
<1.6 |
|
Light |
30–39 |
9–11 |
2.4–4.7 |
2.0–3.9 |
1.6–3.1 |
|
Moderate |
40–59 |
12–13 |
4.8–7.1 |
4.0–5.9 |
3.2–4.7 |
|
Vigorous |
60–89 |
14–17 |
7.2–10.1 |
6.0–8.4 |
4.8–6.7 |
|
Near maximum |
≥90 |
≥18 |
≥10.2 |
≥8.5 |
≥6.8 |
Table 3.Estimated MET levels of Seosan, Korea, for the primary prevention group according to walking speed (n=11)
|
Forest terrain |
MET level |
|
2 km/hr |
3 km/hr |
4 km/hr |
|
Uphill |
5.41 |
7.61 |
9.82 |
|
Even |
3.75 |
5.12 |
6.49 |
|
Downhill |
<3.75 |
<5.12 |
<6.49 |
|
Approximate average |
4.30 |
5.91 |
7.60 |
Table 4.Estimated MET levels of Ansan, Korea, for the secondary prevention group according to walking speed (n=17)
|
Forest terrain |
MET level |
|
2 km/hr |
3 km/hr |
4 km/hr |
|
Paved road (uphill) |
3.71 |
5.06 |
6.42 |
|
Boarded path |
|
|
|
|
Uphill |
|
|
|
|
Normal |
3.29 |
4.43 |
5.57 |
|
Steep |
3.98 |
5.47 |
6.96 |
|
Downhill |
<3.37 |
<4.55 |
<5.73 |
|
Hiking trail |
|
|
|
|
Steep uphill |
4.52 |
6.28 |
8.05 |
|
Even |
3.37 |
4.55 |
5.73 |
|
Approximate average |
3.65 |
4.98 |
6.31 |
Table 5.Adverse events during forest hiking
|
Adverse event |
No. of patients |
|
Primary prevention group (n=11) |
Secondary prevention group (n=17) |
|
Heart attack/arrest |
0 |
0 |
|
Syncope |
0 |
0 |
|
Serious dyspnea |
0 |
0 |
|
Serious arrhythmia |
0 |
0 |
|
Hypoglycemia |
0 |
1 |
|
Intermittent claudication |
0 |
1 |
|
Serious fatigue |
0 |
0 |
Table 6.Comparison of results between the two groups (n=28)
|
Variable |
Primary prevention group (n=11) |
Secondary prevention group (n=17) |
|
Before |
After |
Difference |
Before |
After |
Difference |
|
Body weight (kg) |
63.9±8.4 |
61.5±7.6a)
|
–2.4 |
67.8±12.4 |
66.2±12.6 |
–1.6 |
|
Body fat (%) |
34.5±8.2 |
31.9±8.8a)
|
–2.6 |
29.1±7.6 |
26.4±6.8a)
|
–2.7 |
|
Muscle mass (kg) |
22.5±3.7 |
22.7±3.8 |
0.2 |
26.2±4.8 |
26.6±5.0 |
0.4 |
|
SBP (mmHg) |
132.4±7.3 |
123.3±12.4a,b)
|
–9.1 |
120.6±16.8 |
116.9±12.8 |
–3.7 |
|
DBP (mmHg) |
76.4±7.3 |
76.9±9.5a)
|
0.5 |
72.5±10.6 |
70.2±10.1 |
–2.3 |
|
Heart rate (bpm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At rest |
77.2±9.2 |
64.1±8.8a)
|
–13.1 |
70.7±11.9 |
64.5±7.0a)
|
–6.2 |
|
At maximum |
145.2±23.2 |
154.4±26.1a)
|
9.2 |
137.2±23.6 |
143.3±19.9 |
6.1 |
|
TC (mg/dL) |
187.8±43.1 |
179.8±42.1b)
|
–8.0 |
128.8±23.6 |
122.9±18.0 |
–5.9 |
|
LDL-C (mg/dL) |
116.7±40.6 |
105.9±38.2a,b)
|
–11.0 |
65.2±20.6 |
56.0±13.8a)
|
–9.2 |
|
HDL-C (mg/dL) |
56.6±9.1 |
64.6±11.5a)
|
8.0 |
51.4±11.6 |
52.1±12.9 |
0.7 |
|
Triglyceride (mg/dL) |
104.0±36.3 |
94.9±47.6 |
–9.1 |
129.9±93.4 |
112.4±46.7 |
–17.5 |
|
FBG (mg/dL) |
113.4±17.9 |
105.5±15.1 |
–7.9 |
97.4±15.5 |
103.6±26.5 |
6.2 |
|
HbA1C (%) |
5.9±0.6 |
5.8±0.4a)
|
–0.1 |
6.0±0.8 |
5.8±0.7 |
–0.2 |
|
hs-CRP (mg/L) |
1.16±1.38 |
1.20±2.04b)
|
0.04 |
0.4±0.4 |
0.2±0.3a)
|
–0.2 |
|
MET |
9.4±1.8 |
11.7±1.5a)
|
2.3 |
10.8±2.6 |
11.8±2.7a)
|
1.0 |
|
FRS |
11.2±5.1 |
6.5±3.4a)
|
–4.7 |
7.4±3.8 |
7.4±3.9 |
–0.03 |
REFERENCES
- 1. McMahon SR, Ades PA, Thompson PD. The role of cardiac rehabilitation in patients with heart disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2017;27:420–5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Salzwedel A, Jensen K, Rauch B, Doherty P, Metzendorf MI, Hackbusch M, et al. Effectiveness of comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation in coronary artery disease patients treated according to contemporary evidence based medicine: update of the Cardiac Rehabilitation Outcome Study (CROS-II). Eur J Prev Cardiol 2020;27:1756–74.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Li Q, Morimoto K, Kobayashi M, Inagaki H, Katsumata M, Hirata Y, et al. Visiting a forest, but not a city, increases human natural killer activity and expression of anti-cancer proteins. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2008;21:117–27.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Servey JT, Stephens M. Cardiac rehabilitation: improving function and reducing risk. Am Fam Physician 2016;94:37–43.PubMed
- 5. Balady GJ, Williams MA, Ades PA, Bittner V, Comoss P, Foody JM, et al. Core components of cardiac rehabilitation/secondary prevention programs: 2007 update: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Exercise, Cardiac Rehabilitation, and Prevention Committee, the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Councils on Cardiovascular Nursing, Epidemiology and Prevention, and Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism; and the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Circulation 2007;115:2675–82.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Smith SC Jr, Allen J, Blair SN, Bonow RO, Brass LM, Fonarow GC, et al. AHA/ACC guidelines for secondary prevention for patients with coronary and other atherosclerotic vascular disease: 2006 update: endorsed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Circulation 2006;113:2363–72.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Balady GJ, Ades PA, Bittner VA, Franklin BA, Gordon NF, Thomas RJ, et al. Referral, enrollment, and delivery of cardiac rehabilitation/secondary prevention programs at clinical centers and beyond: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011;124:2951–60.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Swiątkiewicz I, Di Somma S, De Fazio L, Mazzilli V, Taub PR. Effectiveness of intensive cardiac rehabilitation in high-risk patients with cardiovascular disease in real-world practice. Nutrients 2021;13:3883. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Yoo RH, Jeong SA. A case study on application of the effect using forest on human health improvement and disease prevention: focusing on the forest therapy certification in Japan. J Korean Inst For Recreat 2009;13:45–51.Article
- 10. Lee JH, Renate BA. Understanding the healing function of urban forests in German cities. J Korean Inst For Recreat 2011;15:81–9.Article
- 11. Kim SC, Han YH, Park KU, Oh HK. Improvement methods of the forest therapeutic function in recreational forest. J Korean Inst For Recreat 2008;12:1–8.PDF
- 12. Cho YM, Shin WS, Yeoun PS, Lee HE. The influence of forest experience program on children from low income families, sociality and depression. J Korean Inst For Recreat 2011;15:69–75.Article
- 13. Park BJ. Experimental approach of therapeutic effect of forest recreation activities: focused on viewing and walking in forest environments [dissertation]. Chungnam National University; 2010.PDF
- 14. Kim G. Relationship between seasonal NVOC concentration and physical environment in Pinus densiflora forest [master’s thesis]. Chungnam National University; 2014.PDF
- 15. Lee JH, Shin WS, Yeoun PS, Yoo RH. The influence of forest scenes on psychophysiological responses. J Korean Soc For Sci 2009;98:88–93.PDF
- 16. Looney DP, Santee WR, Hansen EO, Bonventre PJ, Chalmers CR, Potter AW. Estimating energy expenditure during level, uphill, and downhill walking. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2019;51:1954–60.ArticlePubMed
- 17. American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). ACSM's guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. 10th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2017.
- 18. Jang S. The effect of aerobic and resistance exercise on serum apelin concentration and risk factors of metabolic syndrome in middle aged obese women [master’s thesis]. Yonsei University; 2016.PDF
- 19. Kim S. The effects of carbohydrate mouth rinse on epinephrine concentration and exercise performance in obese middle-aged women during exercise [master’s thesis]. Yonsei University; 2022.PDF
- 20. Noh SG, Paik IY. The effects of different intensive aerobic training on serum omentin-1 concentration and cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged obese women. J Sport Leis Stud 2015;62:841–51.Article
- 21. Kim CJ, Kim HW. Effects of an 8 weeks walking exercise on blood lipid and HbA1c in obese old women. Korean J Sport 2017;15:609–16.PDF
- 22. Tran ZV, Weltman A, Glass GV, Mood DP. The effects of exercise on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis of studies. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1983;15:393–402.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Um HG, Lee SH, Choi CS, Kim TY. The effect of mountain climbing on blood lipid profiles, MDA and SOD in middle aged men. Korean J Sport Sci 2010;19:795–805.PDF
- 24. Jeon YJ. The effects of aerobic exercise on the improvement of cardiovascular disease in elderly metabolic syndrome women. Korean J Sport 2018;16:653–8.PDF
- 25. Kim CH, Lee H. Effects of aerobic exercise duration on body composition, serum density of lipid, diet and metabolic regulation hormone in middle aged obese women. Exerc Sci 2014;23:193–203.Article
- 26. Thompson PD, Yurgalevitch SM, Flynn MM, Zmuda JM, Spannaus-Martin D, Saritelli A, et al. Effect of prolonged exercise training without weight loss on high-density lipoprotein metabolism in overweight men. Metabolism 1997;46:217–23.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Williams PT. Relationship of distance run per week to coronary heart disease risk factors in 8283 male runners: the National Runners’ Health Study. Arch Intern Med 1997;157:191–8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Ridker PM, Rane M. Interleukin-6 signaling and anti-interleukin-6 therapeutics in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 2021;128:1728–46.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Li Y, Zhong X, Cheng G, Zhao C, Zhang L, Hong Y, et al. Hs-CRP and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality risk: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2017;259:75–82.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Zhao H, He Z, Yun H, Wang R, Liu C. A meta-analysis of the effects of different exercise modes on inflammatory response in the elderly. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022;19:10451. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Koh SH, Kim DY, Kang DW, Kim TK, Ha SM. Effect of free weight exercise on IL-6, hs-CRP and IL-10 in elderly women. J Korean Assoc Phys Educ Sport Girls Women 2022;36:99–112.Article
- 32. Koh SH, Kim TK, Son SY, Kim MK, Kim DY. Effect of combined exercise on serum lipids, liver function and inflammatory levels of hs-CRP on elderly women. J Korean Assoc Phys Educ Sport Girls Women 2023;37:179–93.Article
- 33. Kandelouei T, Abbasifard M, Imani D, Aslani S, Razi B, Fasihi M, et al. Effect of statins on serum level of hs-CRP and CRP in patients with cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mediators Inflamm 2022;2022:8732360. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Myers J, McAuley P, Lavie CJ, Despres JP, Arena R, Kokkinos P. Physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness as major markers of cardiovascular risk: their independent and interwoven importance to health status. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2015;57:306–14.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Ross R, Blair SN, Arena R, Church TS, Despres JP, Franklin BA, et al. Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: a case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016;134:e653–99.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Lavie CJ, Thomas RJ, Squires RW, Allison TG, Milani RV. Exercise training and cardiac rehabilitation in primary and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. Mayo Clin Proc 2009;84:373–83.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Myers J, Prakash M, Froelicher V, Do D, Partington S, Atwood JE. Exercise capacity and mortality among men referred for exercise testing. N Engl J Med 2002;346:793–801.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Kavanagh T, Mertens DJ, Hamm LF, Beyene J, Kennedy J, Corey P, et al. Peak oxygen intake and cardiac mortality in women referred for cardiac rehabilitation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42:2139–43.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Roger VL, Jacobsen SJ, Pellikka PA, Miller TD, Bailey KR, Gersh BJ. Prognostic value of treadmill exercise testing: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Circulation 1998;98:2836–41.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Lewis SF, Nylander E, Gad P, Areskog NH. Non-autonomic component in bradycardia of endurance trained men at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 1980;109:297–305.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Levy WC, Cerqueira MD, Harp GD, Johannessen KA, Abrass IB, Schwartz RS, et al. Effect of endurance exercise training on heart rate variability at rest in healthy young and older men. Am J Cardiol 1998;82:1236–41.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Stein PK, Ehsani AA, Domitrovich PP, Kleiger RE, Rottman JN. Effect of exercise training on heart rate variability in healthy older adults. Am Heart J 1999;138(3 Pt 1):567–76.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Goldsmith RL. A comparison of parasympathetic activity in endurance trained and untrained men [dissertation]. Teachers College, Columbia University; 1991.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

 , Kee-Chan Joo2
, Kee-Chan Joo2 , Kyung-Su Choi3
, Kyung-Su Choi3 , Dae-Sik Yoon4
, Dae-Sik Yoon4
